I. 심실빈맥(ventricular tachycardia)의 정의와 분류
◆ 3개 이상의 PVC(심실조기박동)이 100회/분의 이상속도로 연속에서 나타나는 것
1st : stable VT vs unstable VT (저혈압, 흉통, 심부전, 의식의 저하)
⇒ 초기 치료를 결정하는데 중요함
2nd: 심실빈맥의 지속시간
- Sustained VT : 30초 이상, 개입이 필요한 상태임
- Non-sustained VT : 30초 미만, 지속형 대비 기저심질환이 없는 경우가 많음
3rd : 심실빈맥의 형태
· Monomorphic VT
· Polymorphic VT
· Fascicular VT
· Outflow tract VT
· Bidirectional VT
■ VT의 발생기전
- Reentry : scar-related reentry(m/c)
- Triggered activity : early afterdepolarization, delayed afterdepolarization
- Abnormal automaticity
II. 심실빈맥(VT)의 심전도
■ VT 심전도 특징
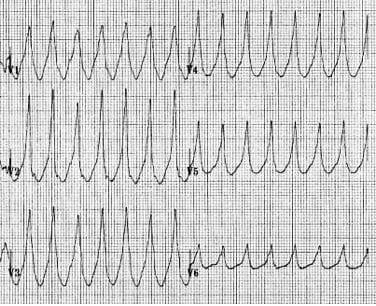
- 매우 규칙적이고, broad complex tachycardia (100-250회/분)
- QRS : wide, bizarre, uniform (단, fusion/capture beat 제외)
■ VT를 시사하는 심전도 특성
- 매우 넓은 complex (160ms 이상)
- 전형적인 LBBB, RBBB의 형태가 없음
- 비정상 axis (northwest axis)를 보임
- AV dissociation(방실해리)
- Capture beat(정상 qrs파)와 Fusion beat(정상 + 비정상 QRS파의 혼합)이 관찰됨

- 흉부유도에서 모두 positive(R) or 모두 negative(QS)를 보임, RS는 보이지 않음

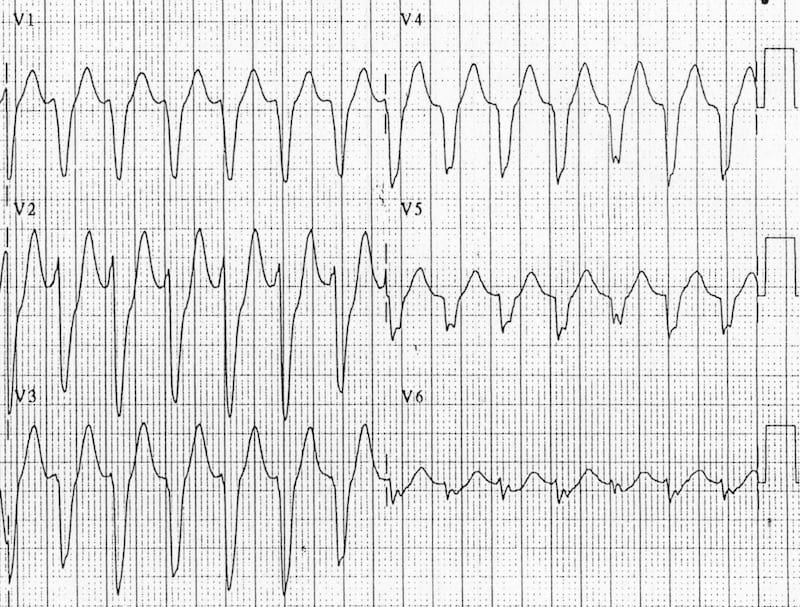
- RSR' complex 에서 왼쪽귀가 더큰 토끼 모양이 나타남

◆ wide QRS SVT(심실상성) 과 VT(심실빈맥) 의 감별
|
SVT(심실상성빈맥)
|
VT(심실빈맥)
|
|
|
|
|
■ Brugada Criteria (wide QRS tachycardia를 precordial lead에서 감별하는 법)
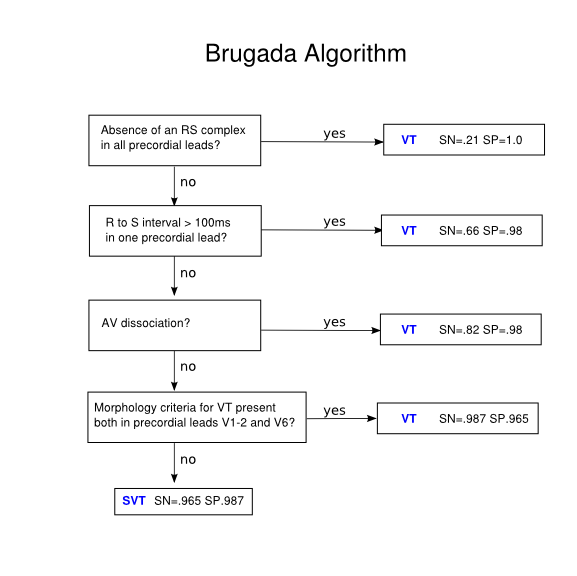
step1. 흉부유도에서 RS pattern 존재?
▶ RS가 없음 ≡ 흉부유도에서 모두 positive or negative ⇒ VT
▶ RS가 존재함 ⇒ step 2


step2. RS 사이간격?
▶ 존재하는 RS에서 R시작~S최저 interval > 100ms ⇒ VT
▶ 존재하는 RS에서 R시작~S최저 interval < 100ms ⇒ step3
▶ 약 3칸을 넘어가는지 아닌지로 판단.

step3. AV dissociation(방실해리)의 존재?
▶ 방실해리 존재시 VT
▶ 없으면 step4

step4. VT를 시사하는 QRS 모양의 존재?
|
|
RBBB형 QRS - V1 : dominant R
|
LBBB형 QRS- V1 : dominant S
|
||
 |
 |
|||
|
V1
|
V6
|
V1
|
V6
|
|
|
SVT
(심실상성)
|
 rSR' triphasic |
 R/S ratio >1 |
 |
 absent Q wave |
|
VT
(심실성)
|
 monophasic R taller Left rabbit qR (biphasic) |
 |
 initial R > 30ms notch or slur of S RS 간격 > 60ms |
 qR complex(위) QS wave(아래) |
III. VT의 치료
■ Nonsustained monomorphic VT (NSVT)
- 증상이 없는경우 경과관찰 (단, congenital long QT syndrome은 X)
- 증상이 있는경우 Beta-blocker
■ Sustained monomorphic VT (SMVT)
- 혈역학적으로 안정적 : Lidocaine, Amiodarone(구조적 심장질환), Procainamide
약물치료 반응X → DC cardioversion
- 혈역학적으로 불안정 (ex.저혈압, 실신, 허혈, CHF) ⇒ DC cardioversion
■ VT의 예방
- ICD 삽입 : 구조적 심장질환이 있는경우 효과적임
- 약물요법 : ICD와 함께 sotalol / amiodarone 추가 가능
- cathter ablation