I. What is Inflammation?
- allows inflammatory cell, plasma proteins, fluid to exit blood vessels and enter the interstitial space
- ACUTE inflammation vs CHRONIC inflammation
■ signs of Inflammation
1) Redness and Warmth
- Due to vasodialtion, which result in increased blood flow
- histamine, prostaglandin, bradykinin → via relaxation of arteriolar smooth muscle
2) Swelling
- Due to leakage of fluid from postcapillary venules into intersitial space
- histamine → endothelial cell contraction
- tissue damage → endothelial cell distruption
3) Pain
- Bradykinin and PGE2 sensitize sensory nerve endings
4) Fever
- Pyrogens(e.g. LPS from bacteria) cause macrophages to release IL-1, TNF
- Cylooxygenase activity in perivascular cells of hypothalamus
- PGE2 → temperture set point ↑
II. Acute Inflammation
- edema and neutrophils in tissue
- response to infection or tissue necrosis
- Innate immunity
| 급성 염증 매개체 |
| TLRs, Arachidonic Acid, Mast cell, Complement, Hagemen factor, Neutrophil, Macrophage |
■ Toll-like receptors (TLRs)
- present on cells of the innate immune system
- activated by pathogen-associated molecular patterns(PAMPs)
- NF-kB activate immune response
- also present on cells of adaptive immunity(lymphocytes) → chronic inflammation
■ Arachidonic acid metabolites (AA)
- released from the phospholipid cell membrane
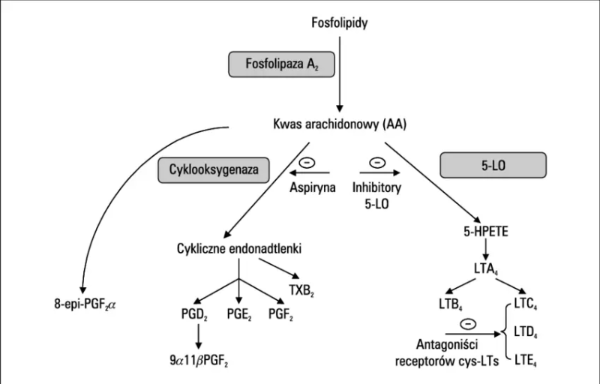
1) Cyclooxygenase ▶ Prostaglandins(PG)
- PGI1, PGD2, PGE2 : vasodilation and increased vascular permeability
- PGE2 : mediates pain and fever
2) 5- Lipoxygenase ▶ Leukotrienes(LT)
- LTB4 : attracts and activates neutrophils
- LTC4, LTD4, LTE4 : vasoconstriction, bronchospasm, vascular permeability (slow anaphylaxis)
■ Mast cells
- widely distributed connective tissue
1) tissue trauma
2) complement proteins C3a and C5a
3) cross linking of IgE by antigen
- Immediate response : histamine granule = vasodilation of arterioles and increase vascular permeability
- Delayed response : Leukotrienes(AA metabolites) production
■ Complement
- proinflammatory serum protein
● activation pathway

i. Classical pathway - C1 binds to IgG or IgM (항원 항체반응)
ii. Alternative pathway - microbial products directly bind
iii. Mannose binding lectin pathway - mannose on microorganism binds to MBL
C3 to C3a (C3 convertase) → C5 to C5a and C5b(C5 convertase) → C5b to C6~9
● Complement product
- C3a and C5a : mast cell degranulation, histamine vasoliation and permeablilty = Anaphlatoxins
- C5a : chemotatic for neutrophils
- C3b : opsonin for phagocytosis
- MAC(C6~9): lyses microbes by creating hole in the membrane
■Factor XII (Hageman factor)

- Inactive proinflammatory protein (produced by Liver)
- activated by exposure to subendothelial or tissue collagen
> Coagulation and fibrinolytic system
> Complement
> Kinin system : bradykinin produce vasodilation and permeability
■ Neutrophil arrival and function
- 호중구의 급성염증에서 이동과 기능 :
■ Macrophage
- 대식세포의 급성염증에서 기능 :
'기초의학 > 해부 병리학' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Cellular Pathology - Amyloidosis | 아밀로이드증의 종류 | 제한성심근병증 (1) | 2025.03.18 |
|---|---|
| Cellular Pathology - Cellular Injury, Necrosis의 종류, Apoptosis (0) | 2025.03.17 |
| Cellular Pathology - Growth Adaptation (0) | 2025.03.16 |
| 장기 이식후 시간에 따른 거부반응 (0) | 2024.11.18 |
| 목 해부학 혈관 Quiz | Internal jugular vein (0) | 2024.11.17 |